The year 2025 marks a historic turning point in global energy history — renewable energy sources have officially overtaken coal as the world’s largest source of electricity generation. This shift represents more than just a milestone; it signals the beginning of a cleaner, more sustainable energy future.
In this article, we’ll explore how renewables surpassed coal, what’s driving this transformation, and what it means for the future of global energy systems, economies, and the environment.
The Global Energy Shift: Renewables Surpass Coal
According to recent data from the International Energy Agency (IEA), renewables — including solar, wind, hydro, and bioenergy — now account for over 40% of global electricity production, surpassing coal for the first time in history.
This growth is fueled by a combination of factors:
- Falling costs of solar and wind technology
- Strong government policies and climate goals
- Growing investment from private and institutional sectors
- Improved energy storage solutions and smart grids
The Decline of Coal Power
Coal, once the backbone of global electricity, is losing ground rapidly. Aging infrastructure, environmental regulations, and rising carbon costs have made coal plants less competitive. Major economies such as the U.S., EU, China, and India are retiring old coal plants and replacing them with cleaner alternatives.
The transition is not only technological but also economic and political, reshaping how nations plan their energy strategies for decades to come.
Why Renewables Are Dominating the Power Landscape
1. Rapid Technological Advancements
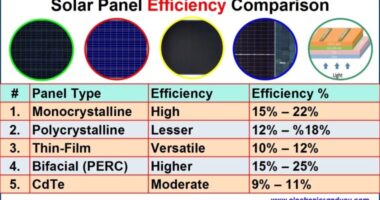
In the last decade, solar panel efficiency has increased from around 15% to over 23%, while wind turbines have doubled in capacity. These innovations mean more power from the same area and lower production costs per kilowatt-hour (kWh).
Furthermore, battery storage systems — such as lithium-ion and solid-state batteries — allow renewable energy to be stored for nighttime or low-wind conditions, making it a reliable 24/7 power source.
2. Falling Costs of Renewable Energy
The cost of solar energy has dropped by over 85% since 2010, and onshore wind by more than 60%. This sharp decline makes renewables the cheapest source of new electricity in many countries.
In 2025, a growing number of nations are experiencing grid parity, meaning renewable energy costs the same or less than fossil fuels, even without subsidies.
3. Global Climate Commitments
The Paris Agreement and recent COP climate summits have accelerated the transition to cleaner energy. Governments are implementing carbon taxes, renewable energy targets, and incentives for green technologies.
Countries like Germany, Japan, and the U.S. have pledged to achieve net-zero emissions by 2050, making renewable investment not just an environmental goal but also an economic necessity.
The Economic Impact of Renewables Overtaking Coal
Job Creation and New Industries
The renewable energy sector is one of the fastest-growing job markets globally. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), the industry now employs more than 14 million people worldwide.
Jobs are being created in:
- Solar and wind installation
- Energy storage production
- Grid modernization
- Green hydrogen and bioenergy technologies
This surge in employment contrasts sharply with the decline of coal mining jobs, which continue to shrink due to automation and plant closures.
Attracting Investment
Investors are shifting focus toward clean energy portfolios. In 2025, renewable energy investment surpassed $1.3 trillion globally, outpacing fossil fuel investments for the first time.
Institutional investors are increasingly divesting from coal due to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) concerns. This movement is accelerating the clean energy transition even further.
Environmental Benefits: Cleaner Air, Lower Emissions
One of the most profound effects of renewable dominance is the reduction in global CO₂ emissions. As coal consumption drops, so do greenhouse gases, helping slow the pace of global warming.
Key Environmental Benefits Include:
- Cleaner air quality due to less particulate pollution
- Reduced water usage, since solar and wind require minimal cooling
- Lower carbon footprint, especially in electricity generation
- Health improvements, as air pollution–related diseases decline
If the current trend continues, the world could avoid billions of tons of CO₂ emissions by 2030, helping to meet the 1.5°C global temperature target.
Challenges Ahead for Renewable Energy
Despite its success, the renewable revolution faces challenges that must be addressed to ensure stability and scalability.
1. Energy Storage Limitations
While battery technology is improving, large-scale energy storage remains expensive. Grid stability depends on developing affordable, high-capacity batteries or alternative solutions like green hydrogen.
2. Intermittency and Grid Management
Solar and wind are weather-dependent, making power output inconsistent. Smart grid technologies, predictive analytics, and hybrid systems are needed to maintain balance and reliability.
3. Infrastructure and Transmission
Many renewable resources are located far from urban centers. Upgrading transmission lines and power networks will be critical to efficiently transport clean energy where it’s needed most.
The Future of Global Energy: What Comes Next
The transition to renewable energy is irreversible. As technology, policy, and investment continue to align, renewables are expected to provide more than 60% of global electricity by 2040.
Emerging Trends Shaping the Future:
- Green Hydrogen: A promising solution for storing and transporting renewable energy.
- Floating Solar Farms: Maximizing space on lakes and reservoirs.
- AI and Smart Grids: Enhancing efficiency and real-time energy management.
- Community Solar Projects: Allowing households without rooftops to benefit from clean energy.
The energy systems of the future will be decentralized, intelligent, and carbon-free — empowering individuals, communities, and nations to take control of their power supply.
Conclusion
Renewables overtaking coal marks a defining moment in human history — the dawn of a new, sustainable energy era. What was once considered an ambitious goal is now a global reality.
The shift means cleaner air, lower electricity costs, millions of new jobs, and a healthier planet. While challenges remain, innovation and collaboration are pushing the world toward a carbon-free future faster than ever before.
The question is no longer if renewable energy will dominate, but how soon it will power the entire planet.